Hey everyone! Ever fired up your 3D printer for what seemed like a simple project, only to end up with a warped mess or a machine jam that derails your whole day? In 2025, the challenges of 3D printing, like high costs, material quirks, and slow speeds, can turn excitement into frustration, making you wonder if the hype is worth the hassle. These limitations of additive manufacturing often leave beginners scratching their heads and experts tweaking endlessly. But don’t worry; understanding these hurdles is the first step to overcoming them.
Let me share a story that might hit home. Take Jamie, an enthusiastic engineer who’s all about 3D printing prototypes for his side hustle in custom gadgets. Last month, he designed a sleek phone holder, hyped to print it overnight. But halfway through, the filament ran out mid-layer, causing a print failure that wasted hours and materials. Frustrated, he restarted, only to deal with bed adhesion issues—the print wouldn’t stick, leading to more scraps.
Diving deeper, let’s break down the core challenges of 3D printing. At its heart, additive manufacturing builds layer by layer, but this precision comes with trade-offs. Key limitations include material constraints—most printers handle plastics like PLA or ABS, but metals and exotics require pricey setups and can be brittle or toxic.
Speed is another biggie; even in 2025, complex prints take hours or days, limiting scalability for mass production. Accuracy and surface finish often suffer, with visible layers needing post-processing like sanding or vapor smoothing.
Build size restricts big projects, like 3D printed houses, to specialized (and expensive) machines.
Then there’s cost: entry-level printers are affordable, but quality materials and maintenance add up quickly. Environmental impacts, such as plastic waste and energy use, pose sustainability hurdles too. Regulatory snags, like IP concerns for shared designs, complicate things further.
These 3D printing issues aren’t just annoyances; they can stall innovation in fields from healthcare to aerospace.
Challenges of 3D Printing in Materials
Now, for solutions—because every challenge of 3D printing has a workaround. Start with materials: the limitations of additive manufacturing here stem from variety and properties. To tackle this, opt for hybrid printers that handle multiple filaments, or explore bio-based options like recycled PLA to cut environmental woes. Services like Shapeways offer access to advanced materials without owning pricey gear, making custom 3D prints feasible for hobbyists. For engineers facing brittleness, software like Autodesk Fusion simulates stress tests pre-print, avoiding failures. This approach turns material limits into manageable choices, boosting reliability.
Challenges of 3D Printing in Speed and Scalability
Speed and scalability are classic 3D printing issues, with prints dragging on for intricate designs. Solutions? Upgrade to faster printers like those with CoreXY mechanics or multi-nozzle systems, cutting times by 50%. For production, hybrid manufacturing combines 3D printing with CNC for efficiency. Cloud-based farms allow scaling via on-demand services, ideal for 3D printing miniatures or prototypes without solo bottlenecks. These fixes make additive manufacturing more viable for bigger runs.
Challenges of 3D Printing in Quality and Finish
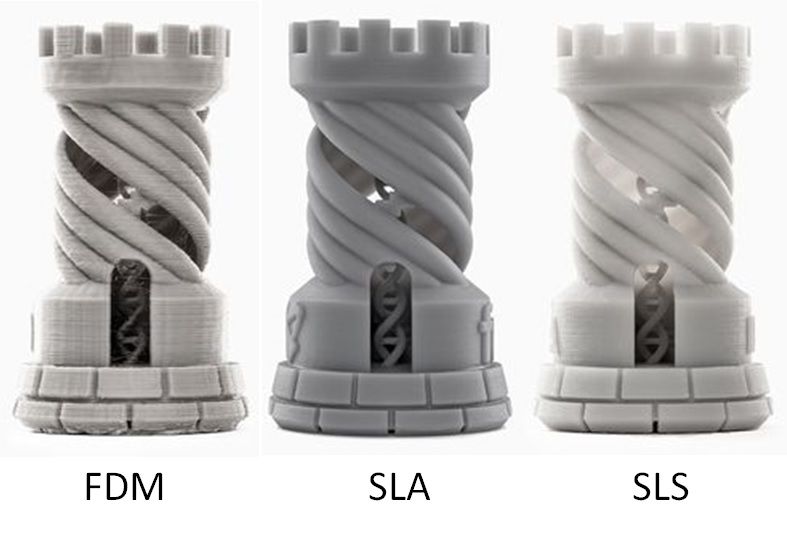
Quality woes, like rough surfaces and inaccuracies, plague many users. Overcome them with better calibration—use auto-leveling beds and precise nozzles. Post-processing tools, such as epoxy coatings or tumblers, smooth finishes effortlessly. For medical or engineering precision, SLA resin printers offer finer details than FDM. This elevates your 3D printing for engineers or cosplay from amateur to pro.
Limitations of Additive Manufacturing in Cost
Cost barriers in 3D printing—high upfront and ongoing expenses—can deter starters. Budget-friendly solutions include open-source printers like Prusa, starting under $300. Bulk-buy materials or recycle failed prints to slash waste. Subscriptions to maker spaces provide access to high-end machines without ownership costs, perfect for tackling challenges of 3D printing on a dime.
Limitations of Additive Manufacturing in Size and Strength
Size limits mean big ideas get scaled down. Counter this with modular designs—print parts and assemble. For strength, reinforce with composites or infills; fiber-filled filaments boost durability for 3D printing prototypes. Emerging large-format printers, like those for 3D printed houses, are becoming more accessible.
Limitations of 3D Printing in Sustainability
Sustainability and regs are growing concerns. Go green with biodegradable filaments and energy-efficient printers. For IP, use licensed designs from sites like Thingiverse. Stay compliant by following FDA guidelines for 3D printing medical items.
To add extra value, here are tips to navigate these hurdles. Calibrate regularly to avoid adhesion fails—apps like OctoPrint help monitor remotely. For materials, experiment with PETG for flexibility. Check videos like “Overcoming 3D Printing Failures 2025” on YouTube for visual fixes. Read articles on ScienceDirect for deep dives into sustainable printing. Or explore Reddit threads for community hacks on 3D printing issues. These resources turn limitations into learning opportunities, whether for 3D printing for cosplay or professional use.
Conclusion
In summary, while the challenges of 3D printing—like costs, materials, and speed—persist in 2025, smart solutions make them surmountable. Embrace these limitations of additive manufacturing as chances to innovate. Ready to level up? Join a local maker group or try a new filament today—your perfect print awaits!