3D Printing Basics: A Complete Guide to Additive Manufacturing

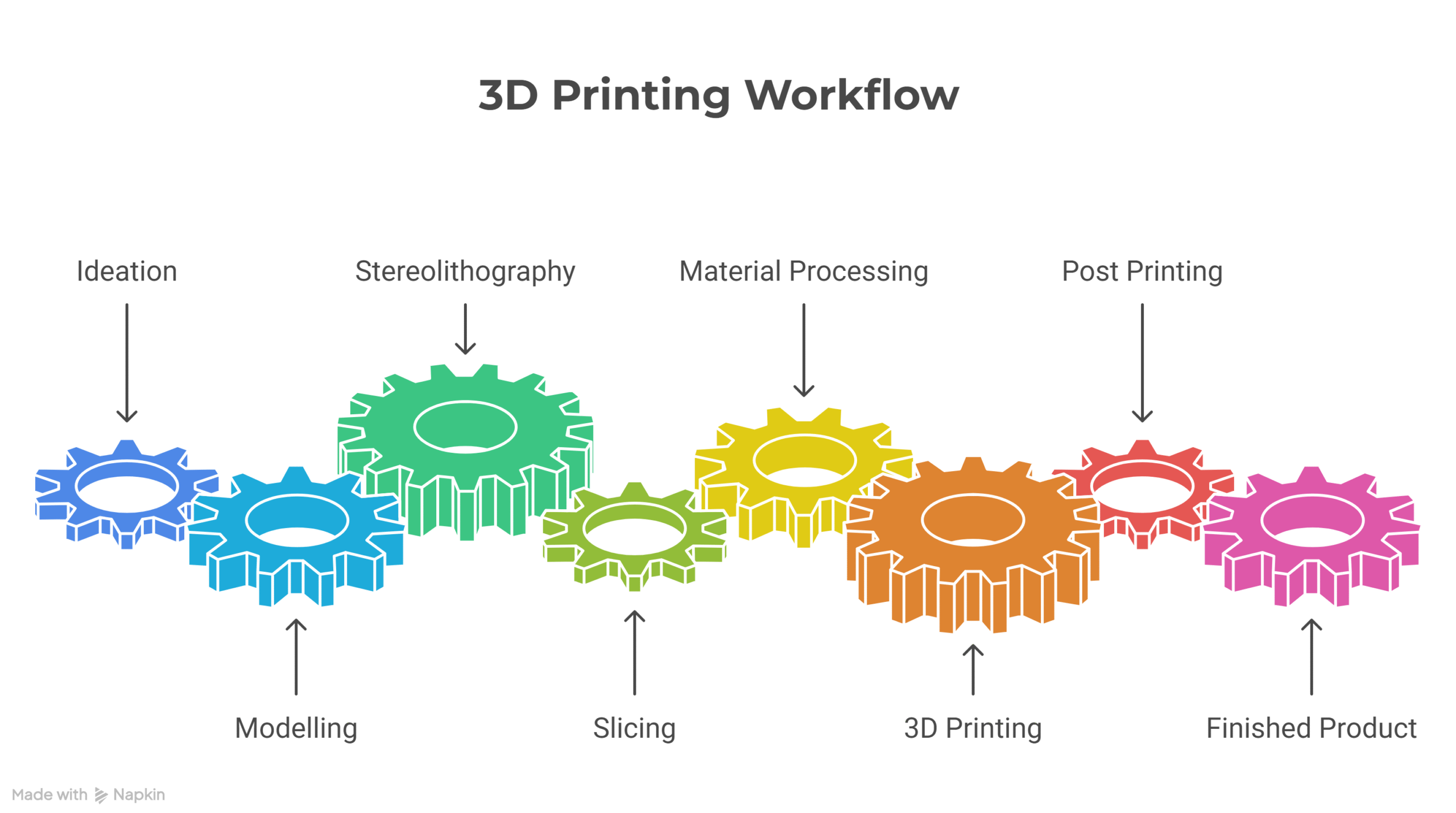
3Dprinting is transforming modern manufacturing across industries. Also known as additive manufacturing, it allows objects to be built layer by layer from digital designs. Beginners can quickly learn how 3D printing works and why it has become a cornerstone of prototyping and production.From healthcare to aerospace, additive manufacturing enables the creation of functional, customized products that were once impossible with traditional methods.
This guide explains 3D printing fundamentals, technologies, materials, and applications for a complete understanding.
What is 3D Printing?
Definition of 3D Printing
3D printing is the process of creating three-dimensional objects directly from digital models. Printers build objects layer by layer, reducing waste and increasing precision. Understanding this definition is crucial for those exploring additive manufacturing. Learn more about the history and definition of 3D printing.
History and Evolution
The story of 3D printing began in the 1980s with the invention of stereolithography. Over the years, additive manufacturing grew from a niche process into a mainstream solution for prototyping and production. Today, FDM 3D printing and SLA printing are among the most widely used methods across industries.Read more about the history of 3D printing.
Importance in Modern Manufacturing
Industries rely on 3D printing for its speed, precision, and flexibility. Additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping, customization, and significant cost savings compared to traditional manufacturing. Explore applications of additive manufacturing.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
Step-by-Step 3D Printing Process
The 3D printing process begins with a digital 3D model created in CAD software. The design is sliced into layers, and the printer follows these instructions to build the object. Each layer fuses with the next, creating a strong and precise product. Learn more about the 3D printing process.
Tools and Software for 3D Printing
Software like Cura, PrusaSlicer, and SolidWorks help create and prepare 3D models. Choosing the right software is essential for efficient additive manufacturing and high-quality outcomes. Read our beginner’s guide to 3D printing.
Key Concepts and Terminology in 3D Printing
Common 3D Printing Terms
Important terms include filament, infill, nozzle diameter, supports, and layer height.FDM 3D printing relies on filaments like PLA or ABS, while SLA printing uses liquid resins to create smooth, detailed models. Explore essential 3D printing terms and concepts.
Beginner-Friendly Glossary
A glossary helps beginners understand terms like additive manufacturing, overhangs, and print speed. Knowing these basics makes 3D printing more accessible.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
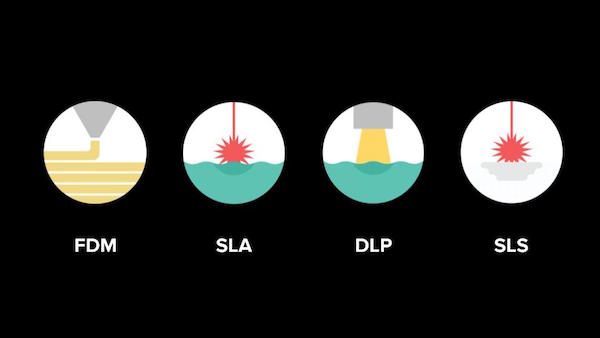
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM is one of the most affordable and beginner-friendly technologies. It works by extruding melted filament layer by layer. Learn more about FDM vs SLA.
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA uses lasers to cure liquid resin, producing parts with high detail and smooth finishes. SLA printing is preferred for precise prototypes compared to FDM 3D printing.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS fuses powdered material using lasers, making it ideal for strong and functional parts used in industries. Comparing these methods helps in selecting the best technology for your project.
Materials Used in 3D Printing
Plastics and Filaments
Common plastics include PLA, ABS, and PETG, which are popular for FDM 3D printing. Specialty filaments add flexibility and durability. Discover different 3D printing materials.
Metals and Composites
Advanced additive manufacturing processes use titanium, stainless steel, and carbon fiber composites for industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Material
The choice of 3D printing materials affects strength, flexibility, and finish. Selecting the right one ensures the product meets its purpose.

Applications and Benefits of 3D Printing
Industry Applications
Healthcare uses 3D printing for prosthetics, implants, and anatomical models. Automotive and aerospace industries leverage additive manufacturing for lightweight, complex parts and rapid prototyping. Read more about applications of additive manufacturing.
Key Benefits
The benefits of 3D printing include speed, reduced waste, customization, and cost-effectiveness. These advantages drive innovation in nearly every sector.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing
Cost and Technical Limitations
High-quality 3D printers and materials can be expensive. Other challenges include calibration, post-processing, and slower print speeds compared to mass manufacturing.
Material and Scalability Challenges
Not all materials are compatible with every printer, and scaling production can still be a limitation. Learn more about challenges of 3D printing.
Getting Started with 3D Printing: A Beginner’s Guide
Choosing Your First Printer
For beginners, FDM 3D printing is affordable and user-friendly. SLA is better for those who need high detail and smooth finishes.
Recommended Software and Tools
CAD modeling software and slicing tools are essential for preparing digital files. Proper calibration ensures quality printing results. Read our beginner’s guide to 3D printing.
Tips for First Projects
Start with simple models to learn the basics of 3D printing. As experience grows, move on to more complex designs and larger-scale projects.
Future Trends in 3D Printing
Emerging Technologies
Innovations like bioprinting, multi-material printing, and AI-assisted 3D printing are shaping the future of manufacturing.
Predictions for the Next Decade
Additive manufacturing will continue to make production faster, sustainable, and highly customizable. Explore future trends in 3D printing.
Conclusion
3D printing and additive manufacturing are reshaping design, prototyping, and industrial production. By learning about its technologies, materials, applications, and limitations, beginners and professionals alike can harness its full potential. Explore our linked guides on FDM 3D printing, SLA printing, and industry applications to get started. The future of manufacturing is here—powered by 3D printing.
We Are Ready to Help You Now
Our support team is always available to assist you with fast accurate and friendly guidance for any project challenge.
- +91 96295 95638
- sales@arsene3d.com
Our Services
- FDM 3D printing
- SLA 3D printing
- 3D Designing
- 3D Scanning
- Reverse Engineering
- Rapid Prototyping
- Casting & Molding
- Post-Processing